
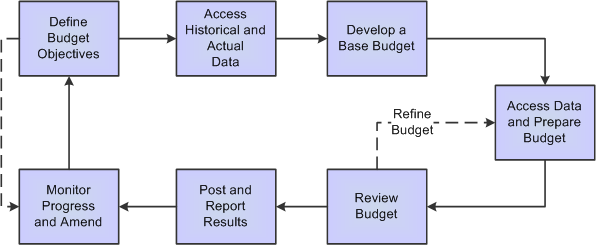

Modern business forecasting began in response to the economic devastation of the Great Depression of the 1930s. Businesses began to regularly use the term “budget” for their finances by the late 1800s. The word “budget” is from the old French word “bougette,” meaning “small purse.” The British government began to use the phrase “open the budget” in the mid-1700s, when the chancellor presented the annual financial statements. However, the definition can be expanded to include all areas of organizational planning including: financial planning and analysis, supply chain planning, sales planning, workforce planning and marketing planning.īasic business accounting practices date as far back as the 1400s, when Venetian investors kept track of their Asian trade expeditions using double-entry bookkeeping, income statements and balance sheets. The process is usually managed by a chief financial officer (CFO) and the finance department. Forecasts are usually adjusted as new information becomes available. Forecasting takes historical data and current market conditions and then makes predictions as to how much revenue an organization can expect to bring in over the next few months or years.It may adjust the budget depending on actual revenues or compare actual financial statements to determine how close they are to meeting or exceeding the budget. Traditionally, a company will designate a fiscal year and create a budget for the year. Budgeting details how the plan will be carried out month to month and covers items such as revenue, expenses, potential cash flow and debt reduction.Planning provides a framework for a business’ financial objectives - typically for the next three to five years.Planning, budgeting and forecasting is typically a three-step process for determining and mapping out an organization’s short- and long-term financial goals:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
